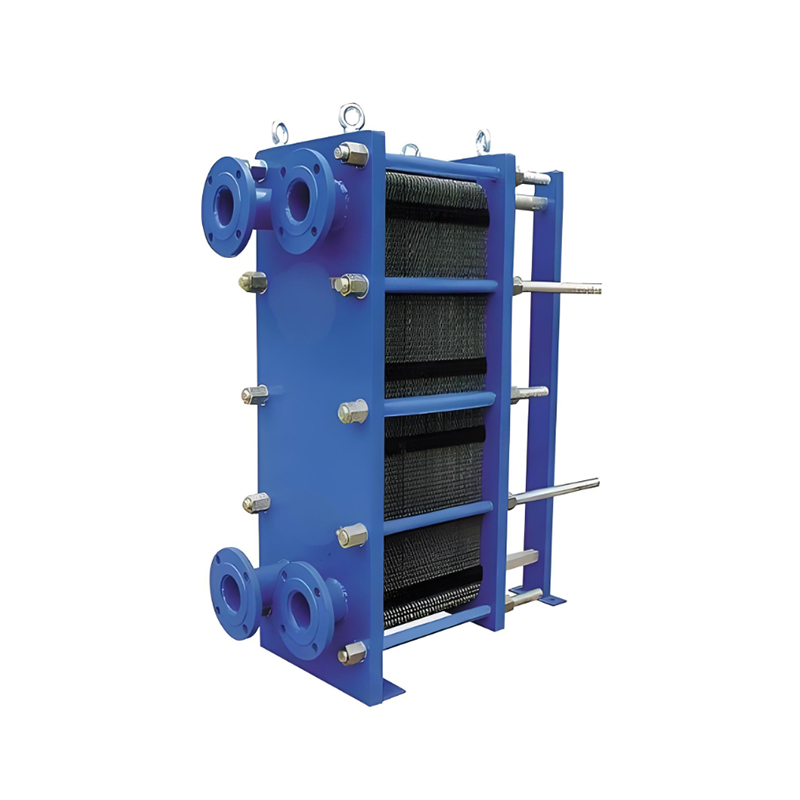
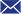
Plate Heat Exchanger
The plate heat exchanger is composed of multiple corrugated plates that are pressed into shape at specific intervals, sealed with gaskets, and compressed within a frame using tightening bolts. The four corner holes of the plates, together with the gaskets, form fluid distribution channels. Through the pipes and manifolds, hot and cold fluids flow through the channels on either side of each plate, maintaining separation and thus enabling efficient heat transfer.
Plate heat exchangers are widely applied across various sectors, including metallurgy, mining, petroleum, chemical processing, power generation, pharmaceuticals, food production, chemical fiber, paper manufacturing, textiles, shipbuilding, and heating systems. They can be utilized for various functions such as heating, cooling, evaporation, condensation, and waste heat recovery.
The following are the design features of plate heat exchangers:
1. Energy Efficiency:
The heat transfer coefficient ranges from 3,000 to 4,500 kcal/m²·°C·h, which is 3 to 5 times the thermal efficiency of shell-and-tube heat exchangers.
2. Compact Structure:
Plate heat exchangers have closely arranged plates. Compared to other types of heat exchangers, they occupy much less space and area. For the same heat exchange surface area, a plate heat exchanger requires only 1/5 of the space needed by a shell-and-tube heat exchanger.
3. Easy Cleaning and Maintenance:
Plate heat exchangers are secured with clamping bolts, making them easy to assemble and disassemble, and allowing for convenient access for cleaning. Additionally, their smooth, clean plate surface and high internal turbulence significantly reduce the potential for fouling.
4. Long Service Life:
Made from stainless steel or titanium alloy plates, plate heat exchangers offer excellent resistance to various corrosive media. Rubber gaskets can be easily replaced, making maintenance simple and cost-effective.
5. Strong Adaptability:
The plates of heat exchangers are independent components, allowing the process configuration to be flexibly adjusted by adding or removing plates as needed. This makes them adaptable to various technical requirements.
6. Leak-Proof Design:
The sealing grooves of plate heat exchangers are equipped with drainage channels, ensuring that different media do not mix. Even in the event of a leak, the media will be discharged externally.
- Contact Us
- Technical Parameters

The company adheres to a corporate philosophy centered on "integrity, cooperation, and innovation." We consistently uphold our brand strategy, which is "market-driven, focused on R&D, meticulously designed, and service-oriented." Our commitment extends to creating an influential high-gravity technology platform and industrial cluster.
Located in a coastal region, Xinchuangxing benefits from a highly active raw material market, which provides a competitive edge in pricing and ensures superior quality. As a Custom Plate Heat Exchanger Manufacturers, We have secured numerous patents and intellectual property rights related to high-gravity technology, demonstrating our exceptionally high technical and innovative capabilities.
-
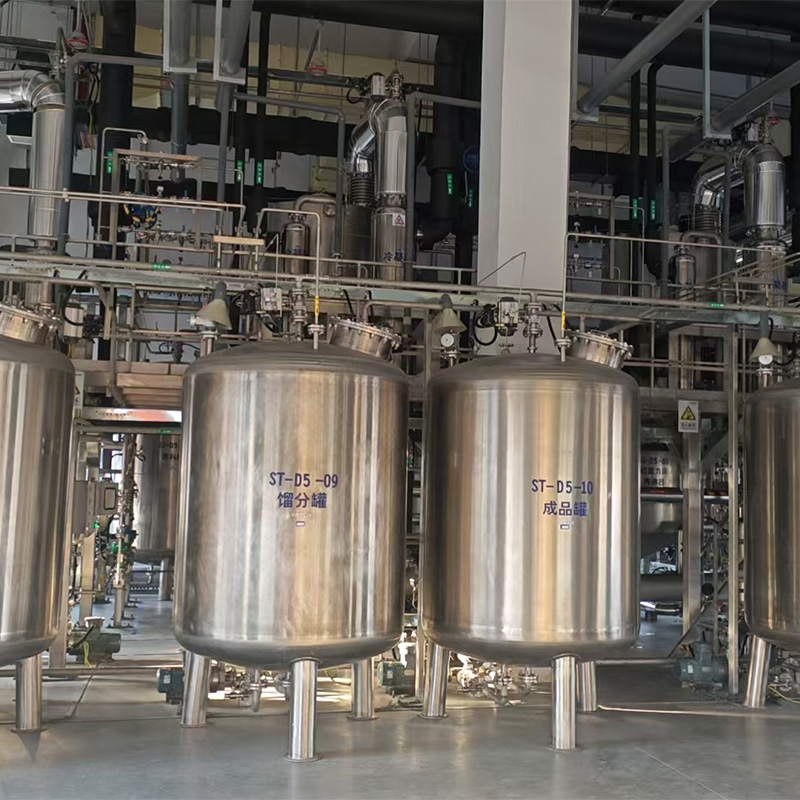
Hygienic Storage Tank is often chosen in critical processes precisely because it must maintain produ...
-
A Hygienic Storage Tank plays a crucial role in industries such as food processing, dairy, and pharm...
-
The stainless steel storage tank system is a foundational component for modern manufacturing in indu...
-
Every chemical processing facility that uses separation technology will encounter operational questi...
-
Integrating a Distillation Unit with an Extraction Unit is a frequent topic of discussion among chem...


 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى