Reactor Temperature Control Challenges in Continuous Systems
Continuous chemical processes often rely on Reactor systems to produce consistent and high-quality products. However, controlling the temperature in these Reactors can be particularly challenging. Improper temperature regulation can reduce reaction efficiency, create safety hazards, and affect downstream processes, including Evaporators used for solvent recovery or product concentration. Zhejiang Xinchuangxing Technology Co., Ltd. specializes in designing Reactor and Evaporator systems that maintain precise temperature control while ensuring energy efficiency and process stability.
In continuous systems, even small temperature fluctuations in Reactors can impact chemical kinetics, resulting in inconsistent yields and product quality. Similarly, Evaporators connected downstream may face variable feed concentrations, which can decrease evaporation efficiency and create scaling or fouling issues if not properly managed.
Common Temperature Control Challenges
Continuous Reactors face several inherent difficulties when it comes to temperature management:
Heat Removal Limitations: Exothermic reactions generate heat that must be efficiently removed to prevent hot spots or thermal runaway.
Uneven Mixing: Poor mixing in continuous flow can create local temperature gradients, resulting in incomplete reactions or by-product formation.
Feed Variability: Variations in reactant temperature, concentration, or flow rate can disrupt the thermal balance of the Reactor.
Environmental Influences: Ambient temperature changes and equipment heat loss or gain can impact Reactor performance, especially in long continuous runs.
Impact on Evaporators and Downstream Processes
Feed Concentration Variation: Reactors operating outside ideal temperature ranges produce inconsistent output, affecting Evaporator performance.
Energy Inefficiency: Evaporators may require more energy to compensate for variations in feed temperature or concentration.
Increased Maintenance: Fluctuating temperatures can accelerate scaling, corrosion, and fouling in downstream Evaporators.
Process Instability: Variability in both Reactor and Evaporator performance can create bottlenecks, reducing overall plant efficiency.
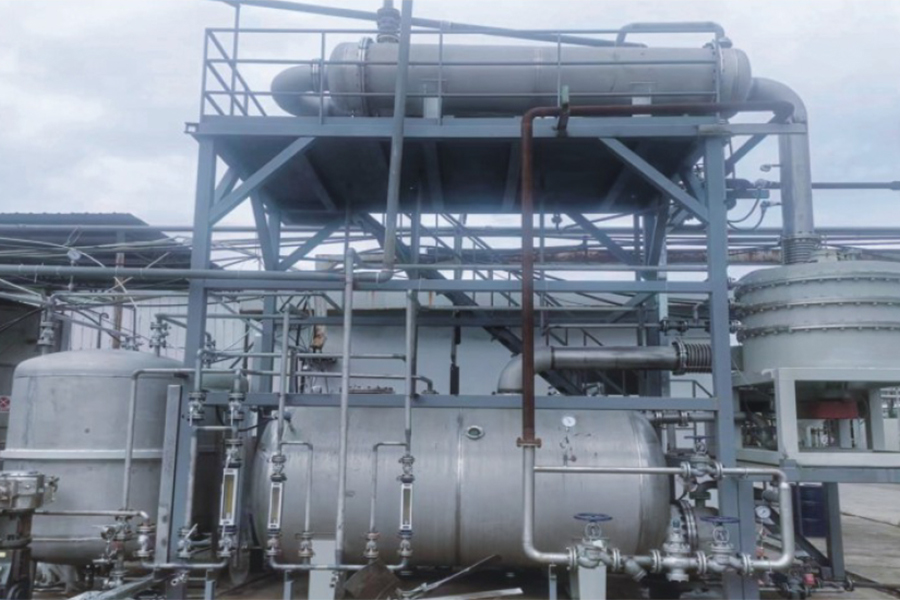

Strategies for Effective Temperature Control
Zhejiang Xinchuangxing Technology Co., Ltd. applies several strategies to ensure continuous Reactors maintain good temperature control:
Advanced Heat Exchange Design: Efficient heat exchangers integrated into Reactor jackets or internal coils remove or supply heat uniformly.
High-Precision Sensors: Real-time monitoring of temperature at multiple points allows automatic adjustments to maintain uniform conditions.
Enhanced Mixing: Optimized impeller design or static mixers ensure uniform heat distribution and reduce hot spots.
Integration with Evaporators: Coordinated control of Reactor and Evaporator systems ensures stable downstream feed and reduces fouling or scaling risk.
High-Gravity Technology Advantage
Our high-gravity technology can also be applied to continuous Reactor systems to improve heat and mass transfer. By creating controlled centrifugal forces, this technology enhances mixing and reduces temperature gradients, providing stable reaction conditions and minimizing the risk of overheating or under-reacting zones. When integrated with downstream Evaporators, this ensures consistent feed concentration, improved energy efficiency, and reduced maintenance requirements.
Temperature control in continuous Reactors is a critical factor influencing reaction efficiency, product consistency, and downstream Evaporator performance. Challenges such as heat removal, uneven mixing, feed variability, and environmental fluctuations can compromise process stability. Zhejiang Xinchuangxing Technology Co., Ltd. offers advanced solutions for Reactor and Evaporator systems, incorporating high-gravity technology, precise monitoring, and optimized design to maintain stable and efficient operation.
Industries running continuous chemical processes can enhance productivity, reduce energy costs, and extend equipment life by addressing Reactor temperature control challenges with integrated solutions. A well-managed system ensures consistent output, smoother operation of Evaporators, and long-term process reliability.


 En
En
 русский
русский Español
Español عربى
عربى